January 30, 2026
When you look at blockchain technology and regular databases for the first time, it feels like they do the same thing: store data. This leads companies to the conclusion that blockchain is a new version of the same old database-centric systems. But in fact, they are radically different things. Traditional databases are optimized for being easy to control and fast and flexible to use, whereas blockchains are decentralized immutable data structures that encourage transparency and trust amongst multiple parties.
The ability to understand how these differ is important for any organization that is considering a technology choice that will affect security, scale, compliance, and the ability to evolve over time.
What Is a Traditional Database Model?
Traditional databases are what power most of today’s applications—CRMs, ERPs, banking systems, ecommerce platforms, and internal dashboards.
At a high level:
- Data is stored centrally
- One organization owns and controls the database
- Admins can read, write, update, or delete records
- Trust is placed in the system owner
Examples include:
- MySQL, PostgreSQL
- Oracle, SQL Server
- MongoDB, Firebase
This model works exceptionally well when:
- One company controls the data
- Speed and performance are critical
- Regulatory compliance requires data control
- Data edits or deletions are necessary
In short, traditional databases are fast, flexible, and efficient—but they depend on centralized trust.
What Makes Blockchain Fundamentally Different?

Instead of the database being held by one, blockchain is a distributed and immutable ledger that is shared among multiple parties who maintain and validate a common set of data.
Key characteristics:
- Data is distributed across many nodes
- Records are immutable (cannot be altered once added)
- Transactions are verified through consensus
Trust is enforced by code and cryptography, not people
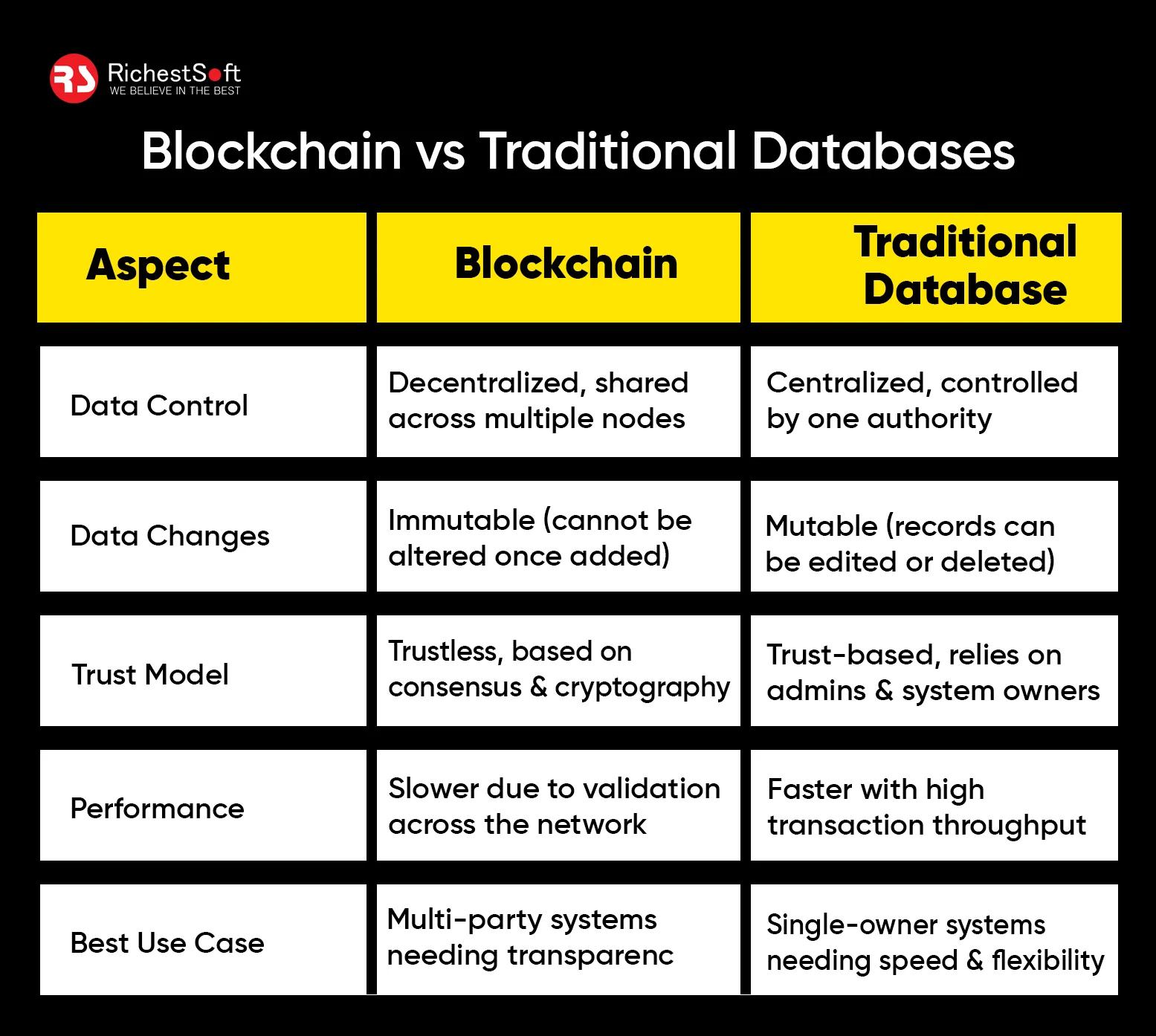
Core Differences: Blockchain vs Traditional Databases

1. Centralization vs Decentralization
Traditional databases are centralized. One organization decides:
- Who accesses the data
- What changes are allowed
- When records are updated or removed
Blockchain is decentralized:
- No single party owns the data
- Multiple participants validate entries
- Changes require network consensus
Business takeaway: Blockchain reduces reliance on intermediaries and single points of failure—ideal for multi-party ecosystems.
2. Data Mutability vs Immutability
In traditional databases:
- Records can be edited or deleted
- Historical changes can be overwritten
- Admin access equals control
In blockchain:
- Once data is written, it’s permanent
- Changes are recorded as new entries
- Full audit trails are preserved forever
Business takeaway: Blockchain is powerful for compliance, auditability, and fraud prevention—but unsuitable for use cases requiring frequent data corrections.
3. Trust Model: Authority vs Consensus
Traditional systems rely on institutional trust:
- You trust the bank
- You trust the platform
- You trust the database admin
Blockchain substitutes trust with mathematical proof:
- Consensus algorithms enable the validation of transactions
- Cryptography guarantees authenticity
- Smart contracts enforce the rules automatically
Business takeaway: Blockchain is useful when its participants don’t trust each other completely but still have to work together.
4. Performance and Scalability
Traditional databases:
- Handle thousands of transactions per second
- Optimized for real-time queries
- Designed for high-performance workloads
Blockchain:
- Slower transaction speeds
- Network-wide validation adds latency
- Scalability is improving—but still limited
Business takeaway: For speed-critical applications, traditional databases win. Blockchain prioritizes integrity over performance.
5. Cost and Complexity
Traditional databases:
- Lower infrastructure costs
- Mature tooling and developer ecosystems
- Easier to maintain and scale
Blockchain:
- Higher initial development cost
- Requires specialized expertise
- Ongoing node, gas, or network fees
Business takeaway: Blockchain should be used strategically, not experimentally, unless there’s a clear ROI.
Blockchain vs Traditional Databases
When Blockchain Makes Business Sense
Blockchain shines when:
- Multiple organizations share data
- Transparency is mandatory
- Data integrity is critical
- Intermediaries increase cost or friction
Common business use cases include:
- Supply chain traceability
- Financial settlements
- Identity verification
- Asset tokenization
- Smart contracts and automation
When Traditional Databases Are the Better Choice
Stick with traditional databases when:
- You need fast read/write performance
- Data needs to be updated or deleted
- One organization owns the system
- Cost efficiency is a priority
Most startups, SaaS platforms, and enterprise apps still rely on traditional databases—and for good reason.
The Smart Approach: Hybrid Architectures
Forward-thinking businesses don’t choose either/or.
They combine:
- Blockchain for trust, verification, and audit trails
- Traditional databases for speed, storage, and analytics
This hybrid approach delivers the best of both worlds without forcing blockchain where it doesn’t belong.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain is not a superior traditional database—it’s just different. The real error companies make isn’t opting for the wrong technology, it’s opting for technology without knowing the problem.
If your enterprise requires transparency to multiple parties, immutable records, or trustless execution, blockchain can be transformative. If not, traditional databases are still the most efficient solution.
At RichestSoft, a blockchain app development company, we enable businesses to make technology decisions that really drive ROI. Our attention is always focused on aligning technology with meaningful, real-world business results – not trends.
FAQ’s
Q1: Does blockchain intend to replace traditional databases?
A: No. Instead of replacing traditional databases, blockchain is a complement to them.
Q2: Why is traditional database faster than blockchain?
A: Since transactions must be validated and agreed upon by the entire network.
Q3: Is it possible to alter or delete blockchain data?
A: No, Blockchain data is immutable.
Q4: Are traditional databases safer than blockchain?
A: It’s more tamper-resistant, but security is implementation-dependent.
Q5: Do all businesses need blockchain?
A: Absolutely not. Only businesses with multi-party trust challenges truly benefit.
 +1 315 210 4488
+1 315 210 4488 +91 99888 06489
+91 99888 06489








